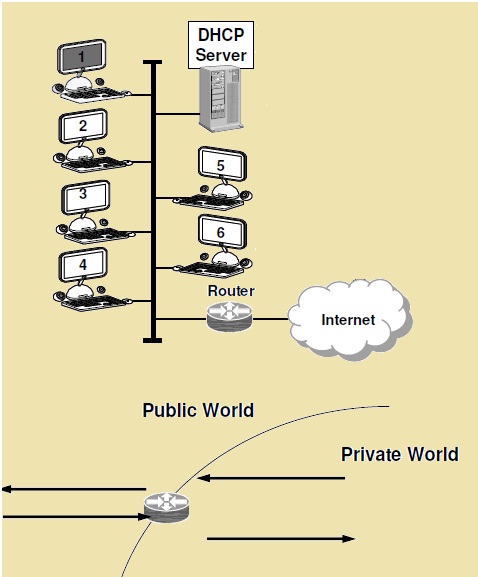
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- DHCP server is configured with a range of addresses
- Host 3 boots up and enters Initialize state
- It broadcasts a DHCP Discover message
- Then enters Select state
- DHCP servers send DHCP offer message
- Host 3 sends a DHCP request to one of the servers
- Host 3 enters the Request state
- DHCP server responds with a DHCP ack (with address)
- Host 3 enters the Bound state, accepting the lease
Network Address Translation – NAT
Operates at the edge of a company network, Converts the private IP addresses into one or more public addresses
Several flavours:
- Fixed private to public relationship – Static NAT
- Demand-based – when a private address needs external access, an address is taken from a pool of public ones and the conversion done at the edge router – Dynamic NAT
- Overload NAT – also called PAT – Port Address Translation
PAT – Port Address Translation
- User on IP Address ‘p’ and port ‘r’ sends packet for the outside
- Router converts this to IP address ‘w’ and port 36578
- Reply comes back for ‘w’ and 36578
- Router converts this to address ‘p’ and port ‘r’