Definition and Effect of Reflection, Diffraction, Scattering and Multipath Propagation in RF Engineering
Reflection Diffraction and Scattering in wireless communication
When any new site has been planned then it should be such a way the effect of Reflection, Diffraction, Scattering and Multipath should be Balance.
Reflection in wireless communication
- Reflections Occurs when a wave impinges upon a smooth surface.
- Dimensions of the surface are large relative to l.
- Reflections occur from the surface of the earth and from buildings and walls.
Diffraction in wireless communication
- Diffraction Occurs when the path is blocked by an object with large dimensions relative to l and sharp irregularities (edges).
- Secondary “wavelets” propagate into the shadowed region.
- Diffraction gives rise to bending of waves around the obstacle.
Scattering in wireless communication
- Scattering Occurs when a wave impinges upon an object with dimensions on the order of l or less, causing the reflected energy to spread out or“scatter” in many directions.
- Small objects such as street lights, signs, & leaves cause scattering
MultiPath in wireless communication
- Multiple Waves Create “Multipath”
- Due to propagation mechanisms, multiple waves arrive at the receiver
- Sometimes this includes a direct Line-of-Sight (LOS) signal
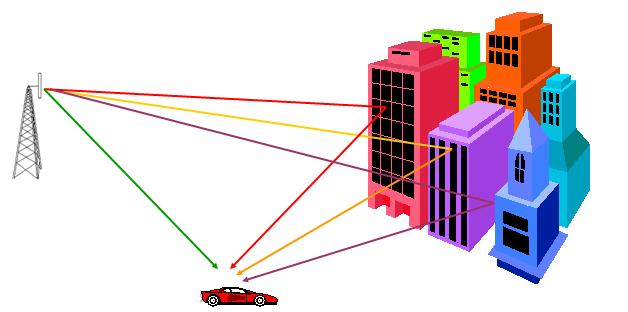
Multipath Propagation in wireless communication
- Multipath propagation causes large and rapid fluctuations in a signal
- These fluctuations are not the same as the propagation path loss.
Multipath causes three major things in wireless communication
- Rapid changes in signal strength over a short distance or time.
- Random frequency modulation due to Doppler Shifts on different multipath signals.
- Time dispersion caused by multipath delays
- These are called “fading effects
- Multipath propagation results in small-scale fading.
Now you understand diffraction has what affect on a wireless signal’s propagation?.