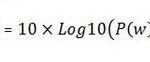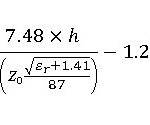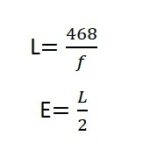Why is GTP used in LTE?
Let me explain GTP and its significance in LTE networks. If you’ve been following our discussions about LTE, you’ll know that it is a highly complex system that enables fast mobile data, voice services, and more. One of the critical protocols used within LTE networks is GTP, which stands for GPRS Tunneling Protocol.
In simple terms, GTP is used for carrying data within the core network and between different parts of the LTE system. It’s essential for the operation of the network, ensuring that data can travel efficiently from one point to another. So why is it so important in LTE? Let’s dive into its specific functions.
GTP plays a crucial role in the communication between the eNodeB (the base station) and the core network in LTE. There are three key types of GTP protocols used in LTE:
- GTP-C (Control): This variant of GTP is used for signaling messages between network elements. It handles tasks like setting up or tearing down connections between nodes, ensuring that the system can maintain efficient communication.
- GTP-U (User Data): This is responsible for the actual user data transfer between the eNodeB and the Serving Gateway (SGW). It tunnels the user’s data packets, enabling seamless connectivity for things like internet browsing, video calls, and more.
- GTP’ (GTP Prime): GTP Prime is an extension of GTP-U, and it is used primarily for monitoring and accounting. It enables the tracking of user data for billing purposes, helping operators measure data usage accurately for their customers.
Now, let’s look at the specific reasons why GTP is crucial in LTE:
- Data Tunneling: As mentioned, GTP tunnels user data from the eNodeB through the SGW and PGW (Packet Gateway) to the internet. This data tunneling ensures that mobile devices maintain their connection as they switch between different parts of the network.
- Efficient Mobility Management: GTP helps manage user mobility, which is a critical aspect of LTE. Whether a user is moving across cells or between different network segments, GTP ensures that their data remains intact, and their session continues without interruption.
- Quality of Service (QoS): With the use of GTP, LTE can apply different quality of service levels to data. This is vital for ensuring that services like video streaming or voice calls maintain high quality even in busy network conditions.
- Scalability: GTP allows for easy scalability in the LTE network. It ensures that the system can grow efficiently, supporting more users and higher data demands without compromising performance.
So, as we see, GTP is a foundational protocol in LTE systems, ensuring that user data is efficiently transmitted, managing mobility, and supporting QoS for different applications. Without GTP, the seamless user experience in LTE would not be possible. It enables a highly functional and dynamic communication system, allowing users to stay connected across various network scenarios, whether moving through different geographical areas or changing between different types of services.
In our previous discussions, we’ve explored how LTE handles high-speed mobile data and advanced services. GTP plays an essential role in these processes, ensuring data is routed efficiently across the network, providing the foundation for mobility and performance in LTE.