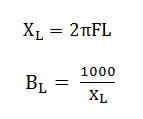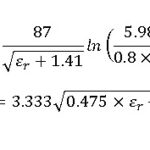A reverse DNS proxy, also known as reverse DNS lookup or reverse DNS resolver, is a server or service that resolves IP addresses to domain names. Unlike forward DNS resolution, which translates domain names to IP addresses, reverse DNS is used to map IP addresses back to domain names. This capability is often used for network troubleshooting, email spam filtering, and security purposes, such as identifying the origin of network traffic or verifying the legitimacy of incoming connections.
A reverse proxy is a server or software application that sits between clients and backend servers, intercepting and forwarding requests on behalf of the clients. It is primarily used to enhance security, improve performance, and ensure high availability of backend services. Reverse proxies can perform tasks such as load balancing, SSL termination, caching, and compression, thereby offloading these functions from backend servers and improving overall system efficiency and resilience.
Reverse DNS, or reverse Domain Name System, serves the purpose of mapping IP addresses to domain names. This process is crucial for various networking tasks, including identifying the origin of emails, verifying the authenticity of network connections, and aiding in network troubleshooting. By associating IP addresses with corresponding domain names, reverse DNS helps maintain the integrity and security of internet communications and assists in maintaining operational reliability across distributed networks.
CDN (Content Delivery Network) and reverse proxy serve distinct purposes despite some overlapping functionalities. A CDN is a distributed network of servers strategically located across various geographic locations. Its primary function is to cache and deliver content (such as images, videos, and web pages) to users based on their geographical proximity, thereby reducing latency and improving content delivery speed. In contrast, a reverse proxy is typically deployed within a single organization’s infrastructure to manage and optimize traffic between clients and internal servers, offering functions like load balancing, SSL termination, and security enhancements.
While reverse proxies offer numerous benefits, such as improved security and performance, they also introduce potential risks if not properly configured or maintained. One risk is misconfiguration, which can lead to unintended exposure of internal systems or sensitive data to unauthorized users. Another risk is the impact on performance if the reverse proxy becomes a bottleneck due to inadequate capacity or inefficient handling of traffic. Additionally, reliance on a reverse proxy for security functions like SSL termination requires careful management to ensure encryption integrity and protection against emerging threats. Proper configuration, regular updates, and monitoring are essential to mitigate these risks and maintain the security and reliability of reverse proxy deployments.