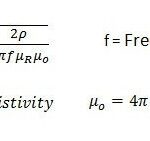What is Positive and Negative SR in LTE?
Today, we are going to learn about Positive and Negative SR in LTE, which are crucial concepts in the scheduling process within the LTE network. Understanding these terms will give you a better idea of how the network manages data transmissions and prioritizes users based on available resources.
In LTE, the Scheduling Request (SR) is used by the User Equipment (UE) to inform the eNodeB (the evolved NodeB) that it has data to send and requires uplink resources. This request allows the eNodeB to determine whether the UE is ready to transmit data and whether it should be scheduled for uplink transmission.
There are two types of SRs that the UE can send: Positive SR and Negative SR. Let’s break them down:
Positive SR
A Positive SR occurs when the UE wants to request uplink resources. This happens when the UE needs to send data but has not been allocated the necessary resources yet. In simpler terms, it’s like the UE signaling to the network, saying, “Hey, I need some resources to transmit data!”
In practical terms, this could happen when the UE has data ready to be sent, and it’s not yet granted access to the uplink channel. The UE sends a Positive SR, which indicates that it wants to transmit data and is requesting resources for uplink transmission. The eNodeB will then handle this request based on resource availability and scheduling conditions.
Positive SRs are essential in situations where the network needs to prioritize certain users or manage the available resources efficiently. They help in ensuring that users who have data to send are given the opportunity to transmit when the network conditions allow it.
Negative SR
On the other hand, a Negative SR happens when the UE signals that it does not require any more uplink resources. This could occur if the UE has no data to send or if the eNodeB has previously allocated resources for transmission, and the UE has completed the data transmission.
A Negative SR can also be seen as a way for the UE to inform the eNodeB that it’s no longer requesting uplink transmission resources. This helps the network avoid unnecessary resource allocation for users who don’t need them. In some cases, the network might automatically adjust based on the Negative SR to free up resources for other users who might need them.
Why are Positive and Negative SR Important?
The use of Positive and Negative SRs allows LTE networks to be more efficient and responsive to the demands of the users. Positive SRs make sure that the eNodeB knows when a user has data ready to send, and Negative SRs help free up resources when they’re no longer needed.
In a sense, the SR mechanism optimizes the way the network allocates resources, ensuring that users who need to send data are prioritized and that the network isn’t wasting resources on idle users.
As we learned in earlier articles, LTE networks rely on dynamic resource management to ensure smooth and efficient communication. The SR mechanism is one such example of how LTE optimizes the way resources are allocated based on user demand.