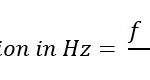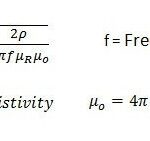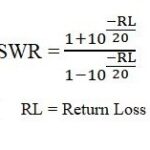What is the Difference Between SNR and CNR?
Today, let me explain the difference between SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) and CNR (Carrier-to-Noise Ratio), two important terms often used in communication systems, especially in wireless networks like LTE. Understanding these two concepts will help you grasp the technical performance of networks and signals.
SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) is a measure used to quantify the ratio of the power of the signal to the power of the background noise. It gives us an idea of how clear and strong the signal is compared to the surrounding noise in the system. The higher the SNR, the better the quality of the communication. This ratio is typically measured in decibels (dB).
In simple terms, when you’re receiving a signal, noise can interfere with the signal, making it difficult to understand or interpret. A higher SNR means a clearer and more reliable signal. For instance, when you’re on a phone call, a high SNR ensures that the voice transmission is clear without distortion from interference or background noise.
CNR (Carrier-to-Noise Ratio) is a similar concept but is specifically focused on the ratio of the carrier signal (the main signal being transmitted) to the noise. It is often used in contexts where the primary focus is on the quality of the carrier signal, such as in radio communications, satellite systems, and LTE networks. CNR is also measured in decibels (dB), just like SNR.
The key difference is that while SNR refers to the overall signal quality (including both the carrier and any other interfering signals), CNR focuses strictly on the ratio between the carrier signal and the noise within the channel. In simpler terms, CNR specifically looks at how strong the desired carrier signal is compared to the noise, whereas SNR looks at the entire environment, including other signals and interference that may affect the reception quality.
Now, let’s break it down further:
- SNR: Measures the overall signal strength relative to noise. It is used in a wide range of communication systems, including mobile networks like LTE.
- CNR: Measures the strength of the carrier signal relative to the noise. It’s especially important in systems where the focus is on the carrier signal, such as satellite communications and radio systems.
Why is this distinction important? For instance, in LTE networks, both SNR and CNR play a role in ensuring that data is transmitted reliably. However, CNR may be more critical in cases where the quality of the carrier signal directly impacts the communication link’s integrity. On the other hand, SNR might be used to determine the overall health of a communication system, as it accounts for interference from multiple sources.
To sum up, while both SNR and CNR measure the relationship between signal strength and noise, they focus on different aspects. SNR gives a broad view of the signal quality in a noisy environment, whereas CNR focuses on the specific quality of the carrier signal relative to the noise. Understanding the distinction between these two is important for optimizing network performance and ensuring reliable communication.