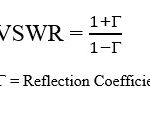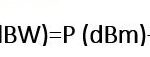What is CN Domain in LTE?
In LTE, the term CN Domain refers to the Core Network (CN) domain, which is a critical component responsible for managing key functions such as user authentication, mobility management, and service delivery. Let me explain this in more detail, so you can understand the role of the CN domain and how it works within the LTE architecture.
The Core Network is essentially the backbone of the LTE system, responsible for connecting mobile users to the internet and other network services. The CN domain handles several functions that are essential for the operation of LTE networks. These functions include user registration, call setup, billing, and maintaining connectivity between the user equipment (UE) and the network. The CN domain is also responsible for managing subscriber data, ensuring that you can seamlessly move between different areas without losing connectivity.
There are two main domains within the LTE core network:
- EPS (Evolved Packet System) Domain: This is the primary domain for data and IP services. It includes the evolved NodeB (eNB) and the Serving Gateway (SGW), and is responsible for handling user-plane traffic such as internet browsing, video streaming, and other data services.
- CS (Circuit-Switched) Domain: This domain handles traditional voice services, including calls and SMS. Although LTE primarily focuses on data services, the CS domain allows for voice calls and text messaging in legacy systems, which are supported by the MSC (Mobile Switching Center) and GMSC (Gateway Mobile Switching Center).
When a device connects to the LTE network, it communicates with the CN domain to request services and manage network sessions. The CN domain interacts with various network entities like the MME (Mobility Management Entity), which is responsible for handling mobility management, session management, and security procedures.
In the context of LTE, the CN domain ensures that your device can seamlessly roam between different network cells while maintaining service quality. For example, when you move from one base station to another, the CN domain ensures that your ongoing data sessions, such as an internet connection, are not interrupted. This also includes managing user authentication and providing IP addresses to your device so it can connect to the internet.
Why is the CN domain essential in LTE? It ensures that the network operates smoothly and that you have a seamless experience when using voice or data services. Even if you are moving between different areas or switching between different types of services (e.g., voice and data), the CN domain is responsible for making sure everything works as expected.
In previous articles, we’ve discussed the key components of LTE networks, including the role of base stations like the eNB and the importance of the Serving Gateway in managing traffic. The CN domain ties all these components together, managing critical functions such as mobility, user authentication, and service continuity.