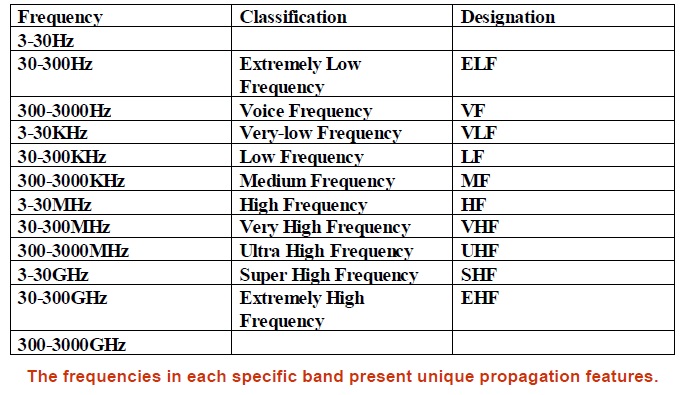
The radio waves are distributed in 3Hz ~ 3000GHz. This spectrum is divided into 12 bands, as shown in the above table. The frequencies in each specific band present unique propagation features: The lower the frequency is, the lower the propagation loss will be, the farther the coverage distance will be, and the stronger the diffraction capability will be.
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic (EM) radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum that are longer than infrared light. They have frequencies from 300 GHz to 3 kHz and corresponding wavelengths from 1 millimeter to 100 kilometers.
However, lower-band frequency resources are stringent and the system capacity is limited, so they are primarily applied to the systems of broadcast, television and paging. The higher-band frequency resources are abundant and the system capacity is large.
however, the higher the frequency is, the higher the propagation loss will be, the shorter the coverage distance will be, and the weaker the diffraction capability will be.
The EM spectrum is generally divided into seven areas where the wavelength decreases and energy and frequency increase.
In addition, the higher the frequency is, the higher the technical difficulty will be, and the higher the system cost will be. The band for purpose of the mobile communication system should allow for both coverage effect and capacity.
Compared with other bands, the UHF band achieves a good tradeoff between the coverage effect and the capacity, and is hence widely applied to the mobile communication field. Nevertheless, with the increase of mobile communication demand, more capacity is required. The mobile communication system is bound to develop toward the high-frequency band.