PDCP layer performs the following functions:
1. Header compression and decompression plane of the user data;
2. Security features:
- encryption and deciphering the user plane and control plane data;
- the protection of the integrity and operation of the plane data;
3. Provide support functions:
- order to delivery and reorder PDU to the layer above a waiver;
- lossless transmission of user plane data associated with the RLC admitted mode.
4. To cancel the user data plane due to timeout.
PDCP layer manages data streams in a plane, and in the plane (or Protocol), only for holders of a radio channel for control (DCCH) or channel dedicated to motion (DTCH). PDCP layer architecture varies the user plane and control plane, as shown in the below 2 figures.
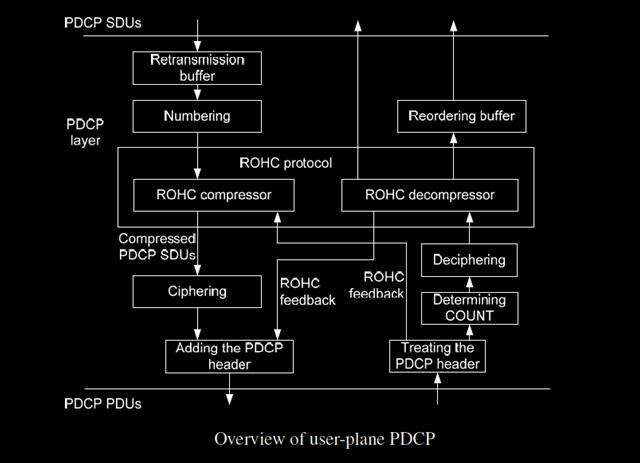
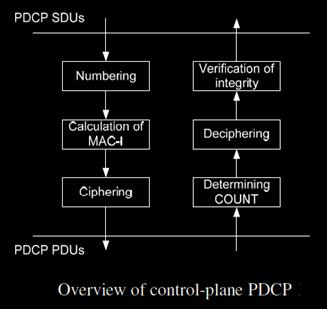
Each one of the main functions is explained in the following subsections. Two different types of PDU PDCP are defined in LTE: PDCP data PDUs and PDCP control PDUs. PDCP data PDUs are used for data plane both the control and the user. PDCP control PDUs are used only to transport the feedback information to the header compression and the PDCP status reports that are used in the event of a transfer of sovereignty and therefore are used only within the user’s plan.
Functions and Architecture of PDCP in LTE
The Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) in LTE is responsible for header compression, encryption, and integrity protection of the data packets exchanged between the user equipment (UE) and the evolved NodeB (eNodeB). PDCP operates in the data link layer of the LTE protocol stack, sitting between the Radio Link Control (RLC) and the IP layer.
The main functions of PDCP include:
- Header Compression: Reducing the overhead in the IP header to minimize transmission overhead and improve efficiency, especially for small data packets.
- Encryption and Integrity Protection: Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data by encrypting and protecting the data payloads, preventing unauthorized access and tampering.
- Packet Duplication Handling: Ensuring that duplicate packets from retransmissions are properly managed, especially when data is sent over unreliable wireless links.
The PDCP architecture consists of two main components: the PDCP entity on both the UE and eNodeB sides. This ensures that data is properly processed, compressed, encrypted, and transmitted between them, contributing to the overall performance and security of the LTE network.