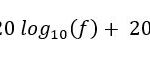In the 5G architecture, the interface between the gNB (Next Generation NodeB) and the UPF (User Plane Function) is referred to as the N3 interface. The N3 interface is a critical link that facilitates communication between the gNB, responsible for radio communication with User Equipment (UE), and the UPF, which handles the user plane data processing in the 5G core network. Here’s a detailed explanation of the N3 interface between gNB and UPF:
- User Plane Function (UPF) Overview:
- The UPF is a key component of the 5G core network responsible for the processing of user plane data. It performs functions such as packet routing, forwarding, and applying policy rules to user data.
- Next Generation NodeB (gNB) Overview:
- The gNB is a central element in the 5G New Radio (NR) network architecture. It handles radio communication with UEs and manages radio resources within its coverage area.
- N3 Interface Functionality:
- The N3 interface enables the exchange of user plane data between the gNB and the UPF. It supports various functions related to the processing and forwarding of user data.
- Data Forwarding:
- One of the primary functions of the N3 interface is to facilitate the forwarding of user plane data between the gNB and the UPF. This includes the transmission of user data packets from the radio access network to the core network and vice versa.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Management:
- The N3 interface plays a crucial role in supporting Quality of Service (QoS) management. It ensures that user plane data is processed according to defined QoS policies, which may include prioritization, traffic shaping, and other parameters to meet specific service requirements.
- Header Compression and Decompression:
- The N3 interface may involve header compression and decompression mechanisms to optimize the efficiency of data transmission. This is particularly important for reducing overhead in the transmission of user data packets.
- Buffering and Flow Control:
- The N3 interface may include mechanisms for buffering and flow control to manage the rate of data transmission between the gNB and the UPF. This helps in handling variations in traffic and ensuring a smooth and controlled flow of user data.
- Transport Protocol:
- The N3 interface uses a transport protocol to facilitate the reliable and efficient transmission of user plane data. This could include protocols such as User Datagram Protocol (UDP) or Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), depending on the specific requirements of the network.
- Data Path Optimization:
- The N3 interface is designed to optimize the data path between the gNB and the UPF. This optimization ensures low-latency, high-throughput, and efficient data transfer, contributing to an enhanced user experience.
- Dynamic Adaptation:
- The N3 interface supports dynamic adaptation mechanisms to adjust to changing network conditions. This includes the ability to adapt to variations in user traffic, network congestion, and other factors that may impact the performance of the data path.
- Interaction with Other Functions:
- The N3 interface interacts with other functions within the 5G core network to ensure end-to-end connectivity and service delivery. This includes coordination with the gNB, session management functions, and other elements in the user plane data path.
- Security Considerations:
- Security mechanisms are implemented within the N3 interface to protect user plane data during transmission. Encryption and integrity protection are applied to ensure the confidentiality and authenticity of the transmitted data.
In summary, the N3 interface between gNB and UPF in 5G is a crucial element for facilitating the exchange of user plane data. It supports functions such as data forwarding, QoS management, header compression, buffering, and dynamic adaptation to optimize the user experience and network efficiency.