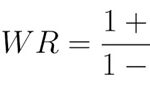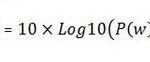What is the Block Error Rate in LTE?
Today, let me explain Block Error Rate (BLER) in LTE, a key performance indicator that directly impacts the quality and reliability of data transmission. If you’ve been reading our previous articles on LTE performance, you’ll recall that LTE is designed to provide high-speed, reliable data transmission. BLER is one of the crucial metrics used to evaluate how effectively the LTE network is delivering this data.
Block Error Rate (BLER) is the percentage of transmitted data blocks that are received incorrectly by the User Equipment (UE). It’s a vital measure because it directly reflects how often transmission errors occur in a communication link. A lower BLER value indicates fewer transmission errors and better network performance, whereas a higher BLER value suggests issues with data integrity, possibly resulting in retransmissions and a poorer user experience.
In LTE, data is transmitted in blocks. These data blocks are sent from the eNodeB (evolved Node B) to the UE. If any of these blocks get corrupted or lost during transmission, they are considered erroneous. BLER is calculated by comparing the number of erroneous blocks to the total number of blocks transmitted. If, for example, one out of every ten blocks is received incorrectly, the BLER would be 10%.
The key here is that BLER helps to measure how reliable the connection is between the eNodeB and the UE. The target BLER in LTE systems is typically set around 10% or lower. If the BLER exceeds this threshold, the system will attempt error correction methods to recover the lost data. These methods include retransmissions, which are part of the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) process, ensuring that the transmission is eventually received correctly. However, excessive retransmissions can cause delays, impacting the overall quality of service.
But how does BLER affect you as a user? Let’s say you’re streaming a video or making a VoIP call over LTE. If the BLER is high, you might experience buffering, delays, or poor call quality. On the other hand, a low BLER indicates that data is being transmitted smoothly, resulting in a more reliable and high-quality user experience.
Several factors influence BLER in LTE, including:
- Signal Quality: A poor signal, caused by distance from the cell tower, obstacles, or interference, can increase the likelihood of transmission errors, thus raising the BLER.
- Channel Conditions: The quality of the wireless channel, influenced by noise, interference, and fading, affects how well the data is transmitted.
- Network Congestion: When the network is overloaded, transmission quality may degrade, leading to higher BLER values.
In previous articles, we’ve covered topics such as signal strength and interference, which also play significant roles in affecting BLER. It’s important to note that while BLER is a key metric, it’s only one of many factors that contribute to overall network performance. If the BLER is too high, it often leads to degraded performance, prompting the LTE system to take corrective actions like retransmissions.
In summary, BLER is a vital measure of data transmission reliability in LTE. By keeping this value low, LTE networks can ensure a smooth, high-quality experience for users. If you’re troubleshooting LTE performance issues, looking at BLER could give you valuable insights into what might be going wrong, whether it’s due to poor signal quality, network congestion, or other factors.