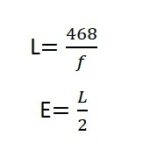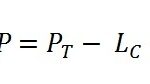NTP (Network Time Protocol) is used for synchronizing the clocks of computer systems over a network. It ensures that all devices have a consistent time reference, which is crucial for various applications and services that rely on accurate timestamping, such as logging, authentication, and distributed databases.
The need for NTP arises from the inherent lack of perfect timekeeping across networked devices. Clocks on different computers can drift due to factors like hardware differences, temperature variations, and network latency. NTP addresses this by continuously adjusting each device’s clock to align with a more accurate reference time provided by designated time servers.
The NTP service provides a means for devices to query time servers and update their internal clocks accordingly. It operates on a client-server model where clients request time information from designated servers. These servers are typically synchronized with highly accurate time sources, such as atomic clocks or GPS receivers, ensuring reliable timekeeping for the entire network.
The function of the NTP protocol includes exchanging timestamps between clients and servers to calculate clock offset and round-trip delay. By analyzing these measurements, NTP algorithms adjust the client’s clock to minimize the difference from the server’s clock. This process ensures that devices maintain accurate time synchronization despite varying network conditions.
Yes, NTP is still widely used across the internet and local networks. Despite advancements in technology, the need for precise time synchronization remains critical for various applications and services, including financial transactions, telecommunications, network security, and distributed computing. NTP continues to evolve with updates to its protocol and enhancements in accuracy and security features to meet the growing demands of modern networks.