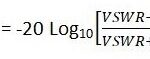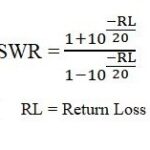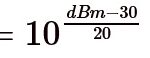What is Mobility Control Information in LTE?
Today, let me walk you through the concept of Mobility Control Information (MCI) in LTE. If you’ve been following our discussions on LTE, you’ll know that one of the key features of this network technology is its ability to handle seamless mobility, ensuring users stay connected while moving between cells. MCI plays a critical role in this process, helping manage the movement of User Equipment (UE) across different network cells.
Mobility Control Information (MCI) refers to the set of parameters exchanged between the network and the UE to support efficient handovers and ensure that the mobile connection remains stable as the user moves from one cell to another. This information includes various data used to control the handover process and ensure that the UE can seamlessly transition between different cells or even between different network technologies like 4G LTE, 3G, or 2G.
The primary role of MCI is to make sure that mobility-related operations, like handovers or cell re-selection, are performed smoothly, without interrupting the user’s experience. For example, when a user moves out of one cell’s coverage area, MCI ensures that the UE knows which new cell it should connect to, and the network can perform the handover to maintain service continuity.
To dive deeper, let’s break down the key components of Mobility Control Information:
- Cell Selection Parameters: These are used to help the UE determine the best cell to connect to when it moves into a new area. The network uses MCI to send these parameters to guide the UE’s decision-making process.
- Handover Parameters: When the UE is about to move from one cell to another, the MCI contains information needed for a successful handover. This includes the target cell’s details and instructions on how the handover should proceed.
- Measurement Configuration: The UE regularly measures the signal strength and quality of surrounding cells to help the network make informed decisions about when to initiate a handover. MCI ensures that the UE has the correct configuration to perform these measurements.
- Timing and Synchronization Information: In order to maintain synchronization between the UE and the network, MCI includes timing information that allows the UE to adjust its communication parameters as it moves between cells.
The information contained within the MCI is essential for ensuring that a handover process is carried out without affecting the user’s data session. This is especially important in scenarios like VoLTE (Voice over LTE) or video streaming, where any interruption in the connection can lead to poor quality or a complete drop in service.
For example, imagine you’re on a call using VoLTE, and you’re walking around the city. As you move from one tower’s coverage area to another, MCI ensures that the handover process happens smoothly so that your call doesn’t drop or lose quality. The network constantly exchanges mobility control information to make sure that this process is seamless.
As we’ve learned in previous articles, LTE aims to provide high-speed, uninterrupted connectivity. Mobility Control Information is a key part of this, as it ensures that even when a user moves between cells, they can maintain a high-quality connection. MCI allows the LTE network to offer the user continuous service, regardless of their location or movement within the network coverage area.