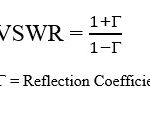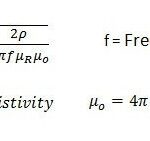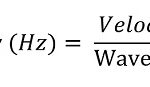Fixed WiMAX offers cost effective point to point and point to multipoint solutions. What makes WiMAX so exciting is the broad range of applications it makes possible but not limited to broadband internet access, T1/E1 substitute for businesses, voice over Internet protocol (VoIP) as telephone company substitute, Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) as cable TV substitute, backhaul for Wi-Fi hotspots and cell phone towers, mobile telephone service, mobile data TV, mobile emergency response services, wireless backhaul as substitute for fiber optic cable.
WiMAX provides fixed, portable or mobile non-line-of sight service from a base station to a subscriber station, also known as customer premise equipment (CPE).
Some goals for WiMAX include a radius of service coverage of 6 miles from a WiMAX base station for point-to-multipoint, non-line-of-sight (see following pages for illustrations and definitions) service. This service should deliver approximately 40 megabits per second (Mbps) for fixed and portable access applications.
That WiMAX cell site should offer enough bandwidth to support hundreds of businesses with T1 speeds and thousands of residential customers with the equivalent of DSL services from one base station.
Fixed WiMAX refers to the IEEE 802.16-2004 standard designed for providing broadband wireless access to stationary or fixed users. It is intended as a wireless alternative to cable or DSL for last-mile connectivity.
Key Features
- Stationary Access: Used for homes or businesses with fixed locations.
- Frequency Bands: Operates typically in licensed frequency bands between 2 GHz and 11 GHz.
- Higher Antenna Gain: Allows use of directional antennas for improved range and reliability.
- Long Range: Supports coverage up to several kilometers due to stable link conditions.
- QoS Support: Enables reliable support for voice, video, and data services.
Applications
Used in rural or underserved areas for high-speed internet, backhaul for cellular networks, or enterprise connectivity.