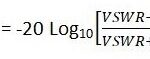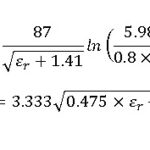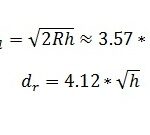What is the Difference Between LTE-A & LTE-A CA?
Let’s dive into the differences between LTE-A (LTE-Advanced) and LTE-A CA (Carrier Aggregation). As we’ve previously discussed, LTE (Long-Term Evolution) is designed to offer high-speed mobile data. However, as the demand for even faster speeds and improved user experiences grew, LTE-A and LTE-A CA emerged as important advancements in mobile communication technology.
LTE-A (LTE-Advanced) is an evolution of the original LTE standard. It was developed to provide higher data rates, better coverage, and improved capacity compared to standard LTE. LTE-A uses a variety of techniques to enhance network performance, including:
- Carrier Aggregation (CA): This allows operators to combine multiple frequency bands, increasing the overall bandwidth and delivering faster speeds.
- Coordinated Multipoint (CoMP): A technology that enhances network efficiency by using multiple transmission points.
- Enhanced Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (eICIC): This helps reduce interference between cells, especially in dense urban environments.
In essence, LTE-A is a more advanced version of LTE that leverages various technologies to deliver better speeds and coverage. It is a crucial step forward in mobile network evolution, aiming to provide users with a more reliable, faster, and efficient experience.
On the other hand, LTE-A CA (Carrier Aggregation) is one of the most significant features within LTE-A. While LTE-A enhances overall network performance, LTE-A CA specifically focuses on combining multiple carrier frequencies to increase data throughput. Here’s how LTE-A CA works:
- Carrier Aggregation: By aggregating two or more frequency bands (carriers), LTE-A CA effectively increases the bandwidth available for a user. This means that data can flow more quickly, allowing for faster download and upload speeds.
- Better Spectrum Utilization: LTE-A CA enables operators to use their spectrum more efficiently, utilizing different frequency bands to improve data rates without the need for more infrastructure.
- Higher Data Rates: With CA, LTE-A can achieve theoretical peak download speeds of up to 3 Gbps, compared to the standard LTE’s maximum of 1 Gbps.
So, while LTE-A is the broader category that includes multiple improvements to LTE, LTE-A CA is a specific technique used to combine multiple carriers and increase network capacity. The key difference here is that LTE-A is a suite of improvements, while LTE-A CA is one particular method within that suite aimed at enhancing bandwidth and improving network performance by utilizing multiple frequency bands simultaneously.
As we discussed in our previous articles, improving network speeds and capacity is essential for supporting the increasing demand for mobile data. LTE-A and LTE-A CA are both crucial to meeting this demand and pushing the limits of what is possible in mobile networks.