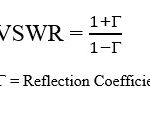What is CSI in LTE?
Let’s dive into CSI (Channel State Information) in LTE, a fundamental concept in wireless communication. If you’re already familiar with how LTE networks function, you know that maintaining a stable and high-quality signal is key to ensuring good performance. CSI plays a crucial role in this process by helping optimize the use of available resources in the network.
In simple terms, CSI refers to the information about the condition of the communication channel between the User Equipment (UE) and the eNodeB (evolved Node B). It essentially describes how well the channel is performing at a given time, including aspects like signal strength, noise levels, and interference. This information allows the LTE network to make smarter decisions about how to allocate resources, such as which frequency or time slot to use for data transmission.
So, why is CSI so important? Let’s take an example: imagine you’re on a phone call or streaming a video over your LTE network. The quality of your call or video stream depends on several factors, including the strength of the signal you’re receiving, the level of interference, and how well the network can handle the data you’re transmitting. CSI helps the network measure these factors in real-time, allowing it to adjust the transmission strategy for optimal performance.
Now, let’s look at how CSI works in LTE:
- Feedback from the User Equipment (UE): The UE sends periodic CSI feedback to the eNodeB, letting the base station know about the channel conditions. This feedback is typically sent using a specific reference signal called the CSI-RS (Channel State Information Reference Signal), which is designed to help the UE measure the channel’s quality accurately.
- Types of CSI: The two main types of CSI in LTE are precoding matrix indicators (PMIs) and rank indicators (RIs). PMIs help the network choose the best transmission method for a given channel, while RIs indicate the number of transmission layers or streams that can be effectively used at any given time.
- Impact on Transmission: With this CSI information, the eNodeB can adjust its transmission parameters to improve the quality of service. For instance, it can decide how many antennas to use (MIMO – Multiple Input Multiple Output), which helps increase throughput and reduce interference.
In a practical sense, CSI helps LTE networks become more adaptive and efficient. Without CSI, the network would be flying blind, not knowing how well the communication channel is performing. But with this information, it can dynamically adjust transmission parameters like modulation schemes, coding rates, and antenna configurations to ensure the best possible user experience.
Additionally, as we’ve seen in previous articles, LTE supports advanced techniques like MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output), which can significantly improve throughput. CSI plays a key role in MIMO by providing the information needed to optimize the use of multiple antennas. By using this feedback, the eNodeB can implement the appropriate strategies to enhance the capacity and reliability of the network.
To summarize, Channel State Information (CSI) is essential for the LTE network to adapt in real-time to changing channel conditions. By providing valuable feedback about the channel’s quality, CSI enables the network to optimize resource allocation, improve throughput, and ensure a high-quality user experience.