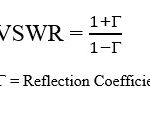Is TD-SCDMA 3G or 4G?
Today, let’s dive into understanding TD-SCDMA and whether it falls under 3G or 4G. We have already talked about different technologies like LTE and its evolution, so now it’s time to explore TD-SCDMA and see how it fits in the world of mobile networks.
What is TD-SCDMA?
TD-SCDMA (Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) is a 3G technology developed primarily in China. It was designed to meet the demands for higher data rates and better network efficiency compared to earlier systems like GSM. TD-SCDMA uses a unique combination of time-division multiplexing and code-division multiplexing to enable users to share the same frequency channel, but at different time slots.
TD-SCDMA in the Context of 3G
TD-SCDMA was primarily used as a part of the IMT-2000 standard for 3G networks, which focused on improving mobile broadband capabilities. It is considered a 3G technology because it offers faster data transfer speeds and better call quality compared to older 2G technologies like GSM. As part of the 3G family, TD-SCDMA supported both voice and high-speed data services, making it a significant step forward in mobile communication.
Comparison with Other 3G Technologies
As we learned in previous discussions, 3G technologies like UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) and CDMA2000 were widely used around the globe. TD-SCDMA was different because it was mainly deployed in China by China Mobile. While UMTS used WCDMA (Wideband CDMA), TD-SCDMA relied on a time-division approach, which offered more efficient use of spectrum in certain conditions.
TD-SCDMA and 4G Technologies
While TD-SCDMA is a 3G technology, it’s important to understand how it relates to 4G. 4G technologies, like LTE, offer significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater overall network efficiency than TD-SCDMA. TD-SCDMA doesn’t meet the requirements for 4G, as 4G standards (such as LTE) focus on even higher data rates and improved quality of service. So, to directly answer the question: TD-SCDMA is not a 4G technology but is rather classified as a 3G technology.
How TD-SCDMA Fits Into the Mobile Evolution
In the broader context of mobile network evolution, TD-SCDMA served as a stepping stone between the older 2G systems and the advanced 4G systems like LTE. It was crucial in expanding mobile internet services in regions where it was deployed, especially in China. But as 4G technologies like LTE became more widespread, TD-SCDMA gradually became less prominent, as it couldn’t support the high data rates needed for modern mobile applications like video streaming, virtual reality, or high-definition gaming.