Based on DCI formats Resource allocation in LTE
Based on DCI formats In LTE Three types of allocation are used:
type 0: DCI formats 1, 2, 2A
type 1: DCI formats 1, 2, 2A
type 2: DCI formats1A, 1B, 1C, 1D
One bit in the header is indicating if DCI formats 1, 2, 2A are of type 0 or type 1.
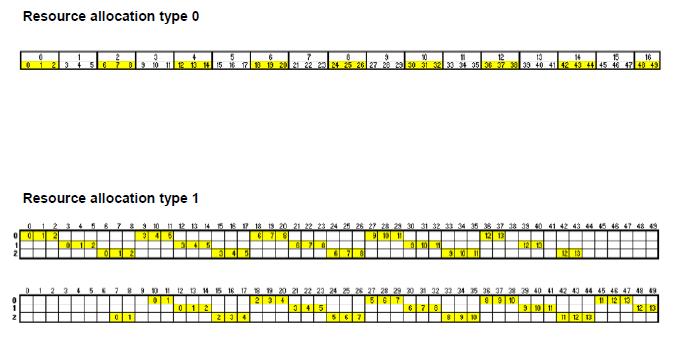
Type 0:
A number of resource blocks forms a resource block group (RBG). A bitmap indicates which RBG(s) is/are allocated in the corresponding TTI. I.e. a group-wise addressing of resources is used. The number of PRBs per group (RBG size) P depends on the cell bandwidth – see Below table.
Type 1:
In type 1 allocation P RGB subsets are in use. There are 3 fields in the allocation to
address single PRBs of an indicated group. Additionally a resource allocation shift
may be applied.
Type 2:
Contiguous allocations are made by type 2. The virtual RBs are localized or distributed. In case of 1A, 1B or 1D the distributed version is signaled by a flag where for 1C this is always the case.
Applicable bandwidths:
– localized: 1 VRB .. system BW
– 1A distributed: 1 .. N_VRB if P-RNTI, RA-RNTI or SI-RNTI scrambled.
– 1B, 1D or 1A distributed, C-RNTI scrambled:1 :: N_VRB (BW = 6 .. 49) and 1 .. 16
(BW = 50..110).
– 1C : N_step .. floor(N_VRB / N_step) * N_step.
N_step = 2 (BW = 6..49), = 4 (BW=50 .. 100).
Based on DCI Formats Resource Allocation in LTE
In LTE, resource allocation is managed through DCI (Downlink Control Information) formats, which specify the resources for data transmission. The DCI format informs the UE about the frequency and time domain resources allocated for uplink or downlink transmission. The eNB uses different DCI formats to communicate scheduling decisions, modulation schemes, and HARQ processes, allowing efficient and flexible resource utilization in the network.