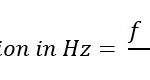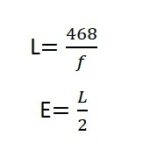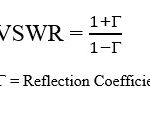What is Hybrid Cell in LTE?
Let me explain hybrid cells in LTE, a concept that plays a significant role in optimizing network performance and providing enhanced coverage and capacity. If you’re familiar with LTE technology, you know how crucial it is to provide consistent and efficient service to users in different scenarios, whether they are in rural, urban, or high-traffic areas. A hybrid cell helps address some of these challenges by integrating both macro and small cells within the LTE network.
A hybrid cell in LTE refers to a cell that combines the benefits of both macro cells and small cells to improve the network’s overall performance. Essentially, it’s a hybrid solution where a small cell (such as a microcell, picocell, or femtocell) is integrated into the existing coverage of a macro cell, either to extend coverage or offload traffic from the macro network to the small cell.
Now, let’s break it down. In traditional LTE networks, macro cells are large cells that provide broad coverage over large geographical areas, but they are limited when it comes to high user density or challenging environments (such as indoor spaces or areas with poor signal strength). This is where small cells come in—they can provide coverage in specific areas where macro cells are less effective, like in crowded stadiums, shopping malls, or offices.
Hybrid cells bridge the gap between these two by combining both cell types to ensure optimal coverage, better capacity, and improved user experience. The integration of macro and small cells enables the network to handle higher user traffic and provide better data rates, especially in areas with high demand for mobile services.
So, how do hybrid cells work in practice? Let me walk you through it:
- Capacity Boost: When traffic is high, the hybrid cell offloads the data demand from the macro cell to the small cell, ensuring that the macro network doesn’t become overloaded.
- Improved Coverage: The small cell within the hybrid setup can provide better coverage in areas where the macro cell signal is weak, such as inside buildings or in urban canyons where signal propagation is difficult.
- Seamless Handover: As a user moves through the network, hybrid cells ensure smooth handovers between macro cells and small cells, providing a consistent user experience even when transitioning between different cell types.
As we’ve seen in previous articles, LTE networks focus on offering high-speed data, low latency, and efficient resource management. Hybrid cells further enhance these goals by enabling more targeted and efficient use of network resources. With the hybrid model, service providers can reduce congestion in highly populated areas while improving coverage in hard-to-reach spots.
But it’s not just about enhancing coverage. Hybrid cells also play a critical role in interference management. By distributing traffic intelligently between macro and small cells, the network can minimize interference, which results in better signal quality and higher user satisfaction. In high-density environments, this is especially important for maintaining a seamless mobile experience as users move between different types of network coverage.
Overall, hybrid cells in LTE offer a smart and efficient way to optimize network performance, providing flexibility to scale as user demand changes. Whether you are in an urban area or an indoor space with weak signals, the hybrid cell ensures that you stay connected with minimal interruptions.
As we continue to see with the evolution of LTE and the transition to 5G, hybrid cells will remain an important component of next-generation mobile networks, helping operators meet growing demands while providing a high-quality service.