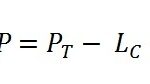What is a Heterogeneous Network in Telecommunication?
A heterogeneous network (HetNet) in telecommunication refers to a network infrastructure that combines different types of technologies and network elements to enhance coverage, capacity, and user experience. It integrates a variety of network components, such as macrocells, small cells (like femtocells, picocells, and microcells), Wi-Fi, and other wireless technologies, to work together seamlessly.
How Does a Heterogeneous Network Work?
In a HetNet, various types of base stations and access technologies are deployed to optimize network performance. These components often use different radio frequencies, bandwidths, and transmission technologies. For example, in a city, macrocells might cover the wide area while small cells fill in the gaps, offering additional capacity in crowded areas like shopping malls or stadiums. Wi-Fi networks can also be integrated to handle data offloading from the cellular network, reducing congestion.
By integrating multiple layers of coverage and capacity, a heterogeneous network aims to provide users with better service, particularly in areas with high traffic demands or poor coverage. The network uses a mix of technologies to ensure seamless handoffs between different network components, allowing for continuous service as users move between areas with different coverage types.
Types of Networks in a Heterogeneous Network
A HetNet typically includes various types of network elements, such as:
- Macrocells: These are traditional, large cellular base stations that provide wide-area coverage.
- Small Cells: These are low-power base stations, including femtocells, picocells, and microcells, designed to enhance capacity and coverage in smaller, localized areas.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi networks can be used for offloading data from cellular networks, providing users with faster data speeds and reducing congestion on the mobile network.
- Backhaul Networks: A HetNet often relies on a mix of fiber, microwave, and other backhaul technologies to connect all these network components.
Benefits of Heterogeneous Networks
Heterogeneous networks offer several benefits that help improve both user experience and overall network performance:
- Improved Coverage: Small cells help extend network coverage to areas with poor signal strength, such as indoors or rural locations.
- Increased Capacity: By adding more small cells and leveraging different access technologies, HetNets can handle more users and data traffic, especially in densely populated areas.
- Offloading Traffic: Wi-Fi offloading reduces the load on the cellular network, allowing users to access the internet more efficiently and reducing network congestion.
- Better User Experience: HetNets enhance the overall user experience by providing faster data speeds, reducing latency, and ensuring seamless handovers between different network layers.
Challenges of Heterogeneous Networks
While HetNets offer numerous advantages, they also come with their own set of challenges:
- Interference Management: Managing interference between different network components, such as small cells and macrocells, can be complex and requires advanced algorithms.
- Network Integration: Integrating different technologies (e.g., 4G, Wi-Fi, 5G) in a HetNet requires sophisticated network planning and coordination to ensure smooth operation.
- Backhaul Demand: The increased number of small cells and other components can place heavy demands on the backhaul network, requiring high-capacity links to maintain performance.
- Security Concerns: The diverse nature of a HetNet makes it more vulnerable to security risks, requiring additional layers of protection and secure communication protocols.
Conclusion
In summary, a heterogeneous network combines different types of wireless technologies and network components to optimize coverage, capacity, and overall network performance. By integrating macrocells, small cells, Wi-Fi, and other technologies, HetNets provide users with better service in both urban and rural areas. While they offer significant benefits, such as improved coverage and offloading capabilities, they also introduce challenges related to interference, integration, and security. Nonetheless, heterogeneous networks are key to supporting the growing demand for high-speed, reliable wireless communication.