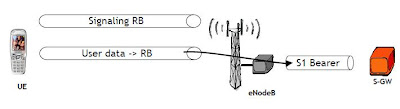
Radio Bearer in LTE
In Long-Term Evolution (LTE) wireless communication, a “Radio Bearer” serves as a crucial link between the user equipment (UE) and the evolved NodeB (eNodeB), facilitating the exchange of data. Radio Bearers are classified into two main categories: Control Radio Bearers (CRBs) and Data Radio Bearers (DRBs).
CRBs are responsible for transmitting control information essential for network management, while DRBs handle user data transfer, ensuring efficient and reliable communication in LTE networks. These bearers play a pivotal role in optimizing resource allocation, managing quality of service (QoS), and enabling seamless connectivity for mobile devices in the LTE ecosystem.
There are 2 types of Radio Bearers (RB) in LTE:
- To carry signaling. There are called the SRB (Signaling Radio Bearer)
- To carry user data. There are associated with an EPS Bearer
In LA1.X, the maximum number of RB per UE is 4
The following types of Radio Bearer are defined:
- SRB1: RRC signaling with high priority
- SRB2: RRC signaling and NAS signaling (lower priority)
- Best Effort: also defined as the default EPS Bearer
- GBR: Radio Bearer with a guaranteed bit rate
- VoIP: Radio bearer to carry the VoIP
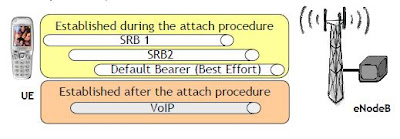
In LA1.X the following combination are supported:
- SRB1
- SRB1+SRB2+Best Effort
- SRB1+SRB2+Best Effort + GBR
- SRB1+SRB2+Best Effort + VoIP
- SRB1+SRB2+Best Effort + Best Effort
At the RRC connection, the eNodeB scheduler creates a context for the UE containing the UEBearerList. this list is limited to 4 per user in LA1.X
Each bearer is identified by the LCID (Logical Channel ID)
Each bearer is associated with QoS parameters like :
- Max bit rate and guaranteed bit rate
- VoIP or not
- H-ARQ usage

Default Bearer vs Dedicated Bearer
- A default bearer is bearer able to carry all kinds of traffic (no filter) without QoS. It is typically created during the attach procedure
- A dedicated bearer is a bearer to carry a specific data flow, identify by the TFT (Traffic Flow Template), with a given QoS.
- Example: Voice, streaming
- It can be established:
- During the Attach procedure (depending on the user profile)
- After the Attach procedure, on demand
The first type, known as Signaling Radio Bearers (SRB), is primarily responsible for carrying signaling information. Signaling information includes critical data for network management, control, and coordination. SRBs ensure that essential control messages, such as connection setup and network handovers, are reliably transmitted between the UE and the eNodeB, guaranteeing seamless communication and network operation. These bearers are vital for maintaining the integrity and stability of LTE networks.
The second type of Radio Bearers in LTE is associated with an Evolved Packet System (EPS) Bearer and is designed to carry user data. These bearers, commonly referred to as Data Radio Bearers (DRB), are responsible for transporting the actual user-generated information, such as voice calls, video streams, and internet data. DRBs play a pivotal role in ensuring that user data is transmitted efficiently and in accordance with quality of service (QoS) requirements. They are instrumental in optimizing resource allocation, bandwidth utilization, and prioritizing different types of data traffic to deliver a seamless and high-quality user experience.
Together, SRBs and DRBs form a comprehensive framework that underpins the reliable and efficient functioning of LTE networks, catering to both control and user data transfer needs.